Shapeless 入门指南(一):自动派生 typeclass 实例
shapeless 是一个类型相关的库,提供了很多有趣的功能。
本文介绍其中一个重要功能:自动派生 typeclass 实例。
Hlist
Shapeless 实现了 HList,不同于 Scala 标准库的 Tuple 的扁平结构,HList 是递归定义的,和标准库 List 类似。
HList 可以简单理解成每个元素类型可以不同 List
简化后的 HList
1 | sealed trait HList |
很容易看出 HList 可以对应到任意 case class,例如1
2case class Foo(a: Int, b: String, c: Boolean)
Int :: String :: Boolean :: HNil
而 shapeless 也提供 Generic 对象实现任意 case class 实例和对应的 HList 之间的转换。
Generic 对象
1 | trait Generic[T] extends Serializable { |
Miles 设计这个对象不局限于 case class,只是很松散的定义 T 和 Repr 之间互相转换方法。
很多人可能疑惑这个方法为什么不设计成两个类型参数 Generic[A, B],这实际上是为了使用 Generic.Aux 绕过编译器限制。
具体可以查看此处
case class 和 HList 互相转换
由于 HList 和 case class 可以一一对应,所以我们很容易想到1
Generic.Aux[Foo, Int :: String :: Boolean :: HNil]
这样的 Generic 对象就可以实现 Foo 和 Int :: String :: Boolean :: HNil 之间的相互转换。
而且 shapeless 会自动使用 macro 生成这样的 Generic 对象
1 | scala> case class Foo(a: Int, b: String, c: Boolean) |
自动派生 typeclass 实例
现在假设我们要设计一个 typeclass
1 | trait Show[A] { |
其功能是可以将任意 case class 实例显示成字符串。为了简化问题,我们定义以下显示规则。
Int类型直接显示为数值Boolean类型直接显示为true或falseString类型用引号包围,例如"str"case class显示为[]包围的属性列表,属性之间逗号隔开[field1, field2, field3...]
我们很容易实现基本类型的 Show 实例
基本类型 Show 实例
1 |
|
现在来看看如何派生任意 case class 的 Show 实例。当然我们可以通过反射或者 macro 实现,这里我们展示 shapeless 如何利用 scala 编译器自动推导出需要实例
任意
case class的Show实例
1 |
|
编译器自动推导出 Show[Foo] 的过程如下
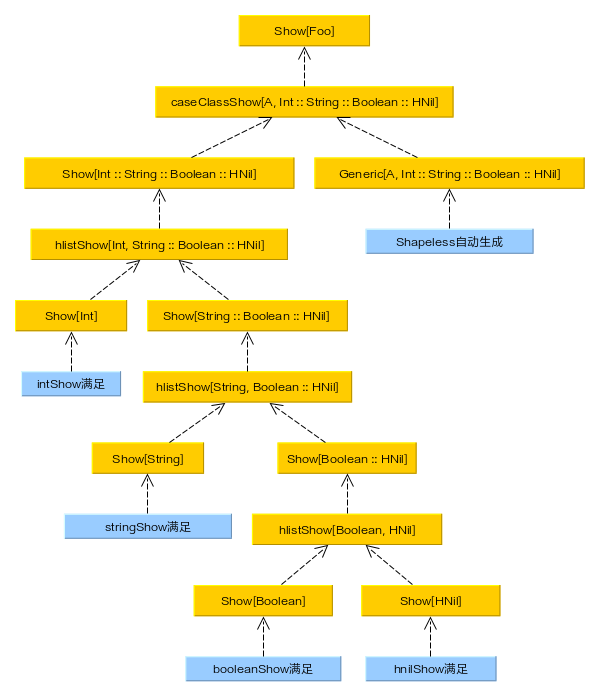
Shapeless 巧妙的利用编译器自动推导功能,推导出了任意 case class 对象的
Show 实例。整个过程虽然理解起来很复杂,但规则却意外的简单:编译器自动推导。
这样实例派生过程就转化成了
Generic 对象和对应 HList 的 typeclass 派生。
当然,现实应用过程中,我们经常需要属性名和递归以及嵌套定义情况,本文中的实现不支持这些场景,后续文章中,我会介绍这些情况处理。